Coenzyme Q10, also known as Ubiquinol or Ubiquinone, is a crucial nutrient present in every cell of our body and plays a pivotal role in energy production. Structurally similar to Vitamin K, Q10, however, is not a vitamin but a vitaminoid, partly produced by the body itself.
Ubiquinol is an essential component of the mitochondrial respiratory chain and is significantly involved in generating ATP, the cellular energy source.
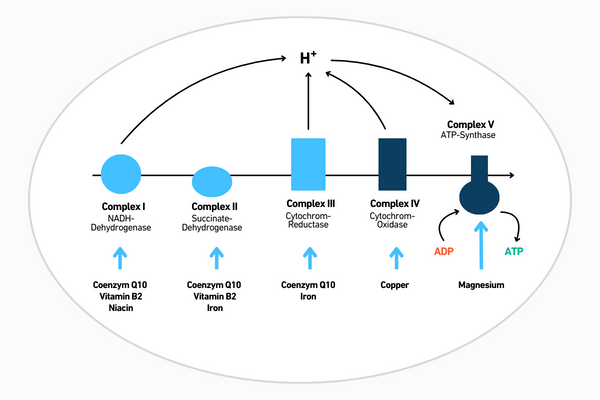 Source: https://www.deutsche-apotheker-zeitung.de/daz-az/2009/daz-48-2009/vitamin-b2-zur-prophylaxevon-migraeneattacken
Source: https://www.deutsche-apotheker-zeitung.de/daz-az/2009/daz-48-2009/vitamin-b2-zur-prophylaxevon-migraeneattackenQ10 and the consequences of deficiency
Q10 exists in two forms in the body:
• Ubiquinol: The active form of Q10, functioning as a potent antioxidant and influencing cellular energy metabolism.
• Ubichinone: The oxidized form of Q10, which in the body is reduced to Ubiquinol and is involved in ATP production.
Even minor deficiencies of more than 25% can lead to structural damage to mitochondria, impairing energy production and transmission within the cell.
As the only fat-soluble antioxidant produced by the body, Coenzyme Q10 protects lipids, DNA, and proteins from free radicals and regenerates important antioxidants like Vitamin E and C. Furthermore, Ubiquinol possesses anti-inflammatory properties and positively influences our blood vessels.
High concentrations of Coenzyme Q10 are found in tissues with high metabolic turnover such as the heart, liver, muscles, and kidneys.
Support the most important muscle in your body — your heart — with Cardio Max by 4Endurance Pro.
Although Q10 is present in foods, the amounts are usually minimal. To intake a significant quantity, for instance, around 2 kg of sardines would need to be consumed, making supplemental intake crucial in diagnosed deficiencies.
The applications of Q10 are diverse, ranging from diabetes mellitus to cardiovascular diseases, migraines, hypertension, and fibromyalgia. Causes of deficiency include malnutrition, absorption disorders, reduced endogenous production, and increased demand due to sports, stress, or certain medical conditions.
Particularly relevant is the use of Q10 in treating with statins for cholesterol reduction, as they also impair the body's production of Q10. Typical symptoms of a Q10 deficiency are muscle pain and trembling. Therefore, supplementation with Q10 during statin intake is essential to address the deficiency.


Cardio Max
Heart muscle support


Coenzyme Q10
Boost cellular energy



Loaded
Vitamins, minerals, adaptogens


Immuno
Anti-inflammation, immunity support
The Role of Coenzyme Q10 in Sports
Q10 plays a crucial role in both recreational and professional sports. During intense physical activities, it supports energy metabolism and contributes to the recovery of heavily stressed muscle groups.
The normal range for Coenzyme Q10 in blood plasma is 0.67-0.99 mg/l, while higher values of over 2.5 mg/l to over 3.0 mg/l are targeted for therapeutic and performance-related goals.
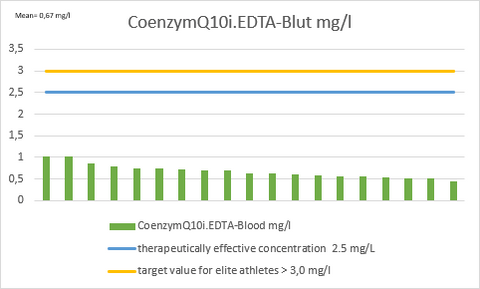 Figure: Coenzyme Q10 assessment in elite athletes 2023 by VerticalMed Tyrol reveals a significantly reduced Coenzyme Q10 supply in elite sports.
Figure: Coenzyme Q10 assessment in elite athletes 2023 by VerticalMed Tyrol reveals a significantly reduced Coenzyme Q10 supply in elite sports.
A deficiency in Coenzyme Q10 can specifically impact various aspects of sports performance, recovery, and overall athletic health:
Reduced Energy Production
Coenzyme Q10 plays a central role in generating energy within mitochondria. A deficiency can lead to diminished ATP production, affecting energy supply for physical activities and resulting in reduced endurance and performance during training.
Increased Fatigue and Reduced Regeneration
Low Q10 levels can extend recovery time after intense training, leading to reduced ability to recover post-exertion, resulting in increased fatigue and longer recovery periods between workouts.
Muscular Discomfort and Damage
A Q10 deficiency might contribute to muscular discomfort, weakness, or damage after intense training, limiting performance and affecting motivation to maintain regular exercise.
Increased Susceptibility to Injuries
Since Coenzyme Q10 plays a role in protecting cells from oxidative stress, a deficiency can make cells more vulnerable to damage. This could impair muscle regeneration and increase the risk of injuries or strain-related damage.
Limited Endurance and Performance
Reduced ATP production due to a Q10 deficiency can lead to faster exhaustion during training. Athletes may not achieve their full potential or face difficulties in training at high intensity for prolonged periods or competing in events.
It is important to note that the effects of a Q10 deficiency can vary individually and depend on various factors such as training volume, intensity, health condition, and diet.
Adequate intake of Coenzyme Q10 can be crucial for athletes to optimize performance, enhance recovery, and reduce the risk of injuries or excessive fatigue.
Conclusion
Overall, Coenzyme Q10 plays an indispensable role in energy metabolism, cellular function, and protection against oxidative stress. Its supplemental use can contribute to supporting health and performance on various levels.
However, despite the current inconclusiveness, the initial premise for Coenzyme Q10 in sports is promising. The increasing interest and ongoing research suggest potential positive implications for athletic performance, recovery, and overall health.
Further exploration and comprehensive studies are necessary to establish a more definitive understanding of the precise impact and optimal utilization of Coenzyme Q10 in the realm of sports science.
Written by: Mag. pharm. Susanne Mair, VerticalMed Tyrol


Cardio Max
Heart muscle support


Coenzyme Q10
Boost cellular energy



Loaded
Vitamins, minerals, adaptogens


Immuno
Anti-inflammation, immunity support
Sources:
Kirkamm, R., Michael, M. (2014). Spezielle Labordiagnostik in der naturkundlichen Praxis (1. Aufl.). Elsevier
Zimmermann, M., Schurgast, H., Burgerstein, Uli P., Handbuch Nährstoffe (13. Aufl.). TRIAS
Drobnic, F., Lizarraga, M. A., Caballero-García, A., & Cordova, A. (2022). Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation and Its Impact on Exercise and Sport Performance in Humans: A Recovery or a Performance-Enhancing Molecule?. Nutrients, 14(9), 1811. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091811
Sánchez-Cuesta, A., Cortés-Rodríguez, A. B., Navas-Enamorado, I., Lekue, J. A., Viar, T., Axpe, M., Navas, P., & López-Lluch, G. (2022). High coenzyme Q10 plasma levels improve stress and damage markers in professional soccer players during competition. International journal for vitamin and nutrition research. Internationale Zeitschrift fur Vitamin- und Ernahrungsforschung. Journal international de vitaminologie et de nutrition, 92(3-4), 192–203. https://doi.org/10.1024/0300-9831/a000659
Moreno-Fernandez, J., Puche-Juarez, M., Toledano, J. M., Chirosa, I., Chirosa, L. J., Pulido-Moran, M., Kajarabille, N., Guisado, I. M., Guisado, R., Diaz-Castro, J., & Ochoa, J. J. (2023). Ubiquinol Short-Term Supplementation Prior to Strenuous Exercise Improves Physical Performance and Diminishes Muscle Damage. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland), 12(6), 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12061193
Fernandes, M. S. S., Fidelis, D. E. D. S., Aidar, F. J., Badicu, G., Greco, G., Cataldi, S., Santos, G. C. J., de Souza, R. F., & Ardigò, L. P. (2023). Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation in Athletes: A Systematic Review. Nutrients, 15(18), 3990. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15183990
https://miraconscience.com/ Zugriff 15.12.2023
https://www.kaneka-ubiquinol.com/ueber-ubiquinol/der-unterschied-zwischen-coenzym-q10-und-ubiquinol/?lang=de




